What Is Heel Discomfort
Overview
Plantar fasciitis: Inflammation of the plantar fascia, the bowstring-like tissue that stretches from the heel bone to the base of the toes. Plantar fasciitis can be due to calcaneal spurs, which typically cause localized tenderness and pain that is made worse by stepping down on the heel. Plantar fasciitis may be related to physical activity overload, abnormal foot mechanics, or may be due to underlying diseases that cause arthritis, such as Reiter disease, ankylosing spondylitis, and diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Treatment is designed to decrease inflammation and avoid reinjury. Icing reduces pain and inflammation. Anti-inflammatory agents, such as ibuprofen and injections of cortisone, can help. Infrequently, surgery is done on chronically inflamed spurs. A donut-shaped shoe insert can take pressure off a calcaneal spur and lessen plantar fasciitis.
Causes
Plantar Fasciitis often leads to heel pain, heel spurs, and/or arch pain. The excessive stretching of the plantar fascia that leads to the inflammation and discomfort can be caused by the following: Over-pronation (flat feet) which results in the arch collapsing upon weight bearing A foot with an unusually high arch A sudden increase in physical activity Excessive weight on the foot, usually attributed to obesity or pregnancy Improperly fitting footwear Over-pronation (flat feet) is the leading cause of plantar fasciitis. Over-pronation occurs in the walking process, when a person's arch collapses upon weight bearing, causing the plantar fascia to be stretched away from the heel bone. With Plantar Fasciitis, the bottom of your foot usually hurts near the inside of the foot where the heel and arch meet. The pain is often acute either first thing in the morning or after a long rest, because while resting the plantar fascia contracts back to its original shape. As the day progresses and the plantar fascia continues to be stretched, the pain often subsides.
Symptoms
A very common complaint of plantar fasciitis is pain in the bottom of the heel. Plantar fasciitis is usually worse in the morning and may improve throughout the day. By the end of the day the pain may be replaced by a dull aching that improves with rest. Most people suffering from plantar fasciitis also complain of increased heel pain after walking for a long period of time.
Diagnosis
Your GP or podiatrist (a healthcare professional who specialises in foot care) may be able to diagnose the cause of your heel pain by asking about your symptoms and examining your heel and foot. You will usually only need further tests if you have additional symptoms that suggest the cause of your heel pain is not inflammation, such as numbness or a tingling sensation in your foot, this could be a sign of nerve damage in your feet and legs (peripheral neuropathy) your foot feels hot and you have a high temperature (fever) of 38C (100.4F) or above - these could be signs of a bone infection, you have stiffness and swelling in your heel, this could be a sign of arthritis. Possible further tests may include blood tests, X-rays - where small doses of radiation are used to detect problems with your bones and tissues, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan or ultrasound scan, which are more detailed scans.
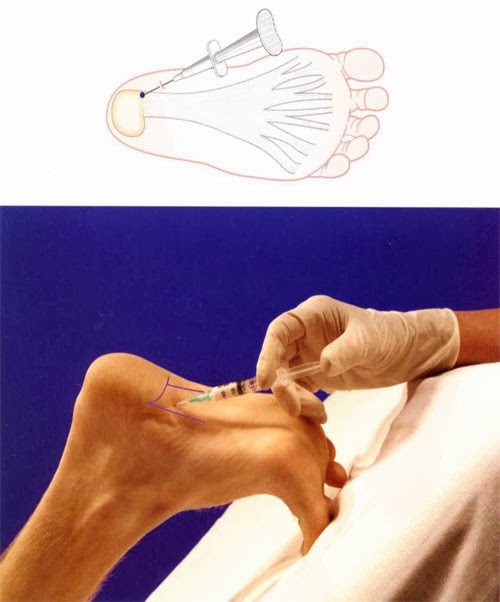
Non Surgical Treatment
No single treatment works best for everyone with plantar fasciitis. But there are many things you can try to help your foot get better. Give your feet a rest. Cut back on activities that make your foot hurt. Try not to walk or run on hard surfaces. To reduce pain and swelling, try putting ice on your heel. Or take an over-the-counter pain reliever like ibuprofen (such as Advil or Motrin) or naproxen (such as Aleve). Do toe stretches camera.gif, calf stretches camera.gif and towel stretches camera.gif several times a day, especially when you first get up in the morning. (For towel stretches, you pull on both ends of a rolled towel that you place under the ball of your foot.) Get a new pair of shoes. Pick shoes with good arch support and a cushioned sole. Or try heel cups or shoe inserts. Use them in both shoes, even if only one foot hurts. If these treatments do not help, your doctor may recommend splints that you wear at night, shots of medicine (such as a steroid) in your heel, or other treatments. You probably will not need surgery. Doctors only suggest it for people who still have pain after trying other treatments for 6 to 12 months. Plantar fasciitis most often occurs because of injuries that have happened over time. With treatment, you will have less pain within a few weeks. But it may take time for the pain to go away completely. It may take a few months to a year. Stay with your treatment. If you don't, you may have constant pain when you stand or walk. The sooner you start treatment, the sooner your feet will stop hurting.
Surgical Treatment
In unusual cases, surgical intervention is necessary for relief of pain. These should only be employed after non-surgical efforts have been used without relief. Generally, such surgical procedures may be completed on an outpatient basis in less than one hour, using local anesthesia or minimal sedation administrated by a trained anesthesiologist. In such cases, the surgeon may remove or release the injured and inflamed fascia, after a small incision is made in the heel. A surgical procedure may also be undertaken to remove bone spurs, sometimes as part of the same surgery addressing the damaged tissue. A cast may be used to immobilize the foot following surgery and crutches provided in order to allow greater mobility while keeping weight off the recovering foot during healing. After removal of the cast, several weeks of physical therapy can be used to speed recovery, reduce swelling and restore flexibility.
Stretching Exercises
You may begin exercising the muscles of your foot right away by gently stretching them as follows. Prone hip extension, Lie on your stomach with your legs straight out behind you. Tighten up your buttocks muscles and lift one leg off the floor about 8 inches. Keep your knee straight. Hold for 5 seconds. Then lower your leg and relax. Do 3 sets of 10. Towel stretch, Sit on a hard surface with one leg stretched out in front of you. Loop a towel around your toes and the ball of your foot and pull the towel toward your body keeping your knee straight. Hold this position for 15 to 30 seconds then relax. Repeat 3 times. When the towel stretch becomes too easy, you may begin doing the standing calf stretch. Standing calf stretch, Facing a wall, put your hands against the wall at about eye level. Keep one leg back with the heel on the floor, and the other leg forward. Turn your back foot slightly inward (as if you were pigeon-toed) as you slowly lean into the wall until you feel a stretch in the back of your calf. Hold for 15 to 30 seconds. Repeat 3 times. Do this exercise several times each day. Sitting plantar fascia stretch, Sit in a chair and cross one foot over your other knee. Grab the base of your toes and pull them back toward your leg until you feel a comfortable stretch. Hold 15 seconds and repeat 3 times. When you can stand comfortably on your injured foot, you can begin standing to stretch the bottom of your foot using the plantar fascia stretch. Achilles stretch, Stand with the ball of one foot on a stair. Reach for the bottom step with your heel until you feel a stretch in the arch of your foot. Hold this position for 15 to 30 seconds and then relax. Repeat 3 times. After you have stretched the bottom muscles of your foot, you can begin strengthening the top muscles of your foot. Frozen can roll, Roll your bare injured foot back and forth from your heel to your mid-arch over a frozen juice can. Repeat for 3 to 5 minutes. This exercise is particularly helpful if done first thing in the morning. Towel pickup, With your heel on the ground, pick up a towel with your toes. Release. Repeat 10 to 20 times. When this gets easy, add more resistance by placing a book or small weight on the towel. Balance and reach exercises, Stand upright next to a chair. This will provide you with balance if needed. Stand on the foot farthest from the chair. Try to raise the arch of your foot while keeping your toes on the floor. Keep your foot in this position and reach forward in front of you with your hand farthest away from the chair, allowing your knee to bend. Repeat this 10 times while maintaining the arch height. This exercise can be made more difficult by reaching farther in front of you. Do 2 sets. Stand in the same position as above. While maintaining your arch height, reach the hand farthest away from the chair across your body toward the chair. The farther you reach, the more challenging the exercise. Do 2 sets of 10. Heel raise, Balance yourself while standing behind a chair or counter. Using the chair to help you, raise your body up onto your toes and hold for 5 seconds. Then slowly lower yourself down without holding onto the chair. Hold onto the chair or counter if you need to. When this exercise becomes less painful, try lowering on one leg only. Repeat 10 times. Do 3 sets of 10. Side-lying leg lift, Lying on your side, tighten the front thigh muscles on your top leg and lift that leg 8 to 10 inches away from the other leg. Keep the leg straight. Do 3 sets of 10.